Step 2: Entity Class and Persistence Unit
To store objects in an ObjectDB database using JPA we need to define an entity class:
- Open the [New Java Class] dialog box, e.g. by right clicking the project node
(in the [Package Explorer] window) and selecting New > Class.
- Enter guest as the package name - use exactly that case sensitive package name.
- Enter Guest as the class name - use exactly that case sensitive class name.
- Click Finish to create the new class.
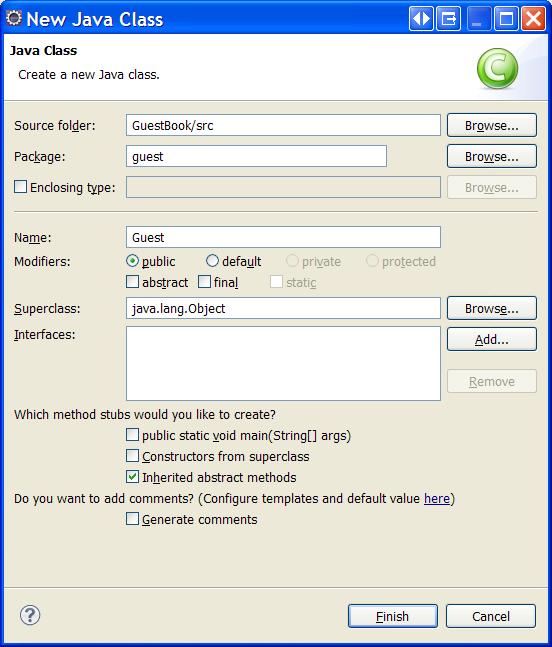
A new class that should represent Guest objects in the database was created in the project (under Java Resources: src > guest).
Use copy and paste to replace the new source file content with the following code:
package guest; import java.io.Serializable; import java.sql.Date; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.Id; @Entity public class Guest implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; // Persistent Fields: @Id @GeneratedValue Long id; private String name; private Date signingDate; // Constructors: public Guest() { } public Guest(String name) { this.name = name; this.signingDate = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()); } // String Representation: @Override public String toString() { return name + " (signed on " + signingDate + ")"; } }
The Guest entity class will represents guests in the database.
We also need to configure JPA by setting a META-INF/persistence.xml file:
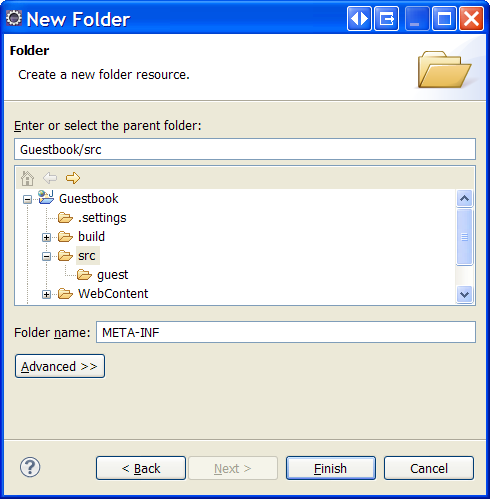
- Open the [New Folder] dialog box, e.g. by right clicking the project node (in the [Project Explorer] window) and selecting New > Folder (or New > Other... > General > Folder and clicking Next).
- Select the project src folder as a parent folder, enter META-INF as a new folder name and click Finish.
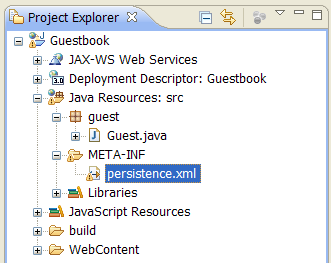
- Right click the new META-INF folder in the [Project Explorer] window, select New > File, enter persistence.xml as file name and click Finish.
- Verify that a new persistence.xml file was created as shown below:
Finally, use copy and paste to copy the following content to the persistence.xml file:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <persistence version="2.0" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence/persistence_2_0.xsd"> <persistence-unit name="GuestbookPU" transaction-type="JTA"> <provider>com.objectdb.jpa.Provider</provider> <properties> <property name="javax.persistence.jdbc.url" value="$objectdb/db/guests.odb"/> <property name="javax.persistence.jdbc.user" value="admin"/> <property name="javax.persistence.jdbc.password" value="admin"/> </properties> </persistence-unit> </persistence>
Now ObjectDB should be used as a JPA provider with the specified database url.
The next step is adding an EJB Session Bean that will manage Guest entities.