Step 2: Define a JPA Entity Class
To store objects in an ObjectDB database using JPA we need to define an entity class:
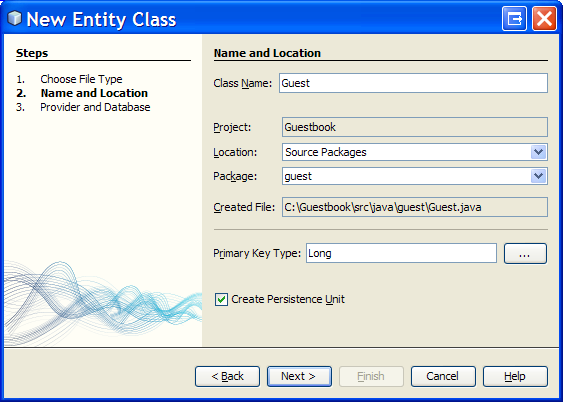
- Open the [New Java Class] dialog box, e.g. by right clicking the project node
(in the [Projects] window) and selecting New > Java Class... - Enter Guest as the class name - use exactly that case sensitive class name.
- Enter guest as the package name - use exactly that case sensitive package name.
- Click Finish to create the new class.
Use copy and paste to replace the new source file content with the following code:
package guest; import java.io.Serializable; import java.sql.Date; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.Id; @Entity public class Guest implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; // Persistent Fields: @Id @GeneratedValue Long id; private String name; private Date signingDate; // Constructors: public Guest() { } public Guest(String name) { this.name = name; this.signingDate = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()); } // String Representation: @Override public String toString() { return name + " (signed on " + signingDate + ")"; } }
The new class should represent Guest objects in the database. Besides the @Entityjakarta.persistence.EntityDeclares that the annotated class is an entity. annotation and the id field (and its annotations) - the Guest class is an ordinary Java class.
The warning that NetBeans displays on the Guest class indicates that a persistence unit definition in an XML file is missing. This is discussed in the ObjectDB Manual. But nevertheless, this class is a valid ObjectDB entity class, despite the warning.
The next step is adding a context listener class that will manage a JPA's EntityManagerFactory representing the ObjectDB database.